Forging: an essential technology for metal processing
Forging process introduction
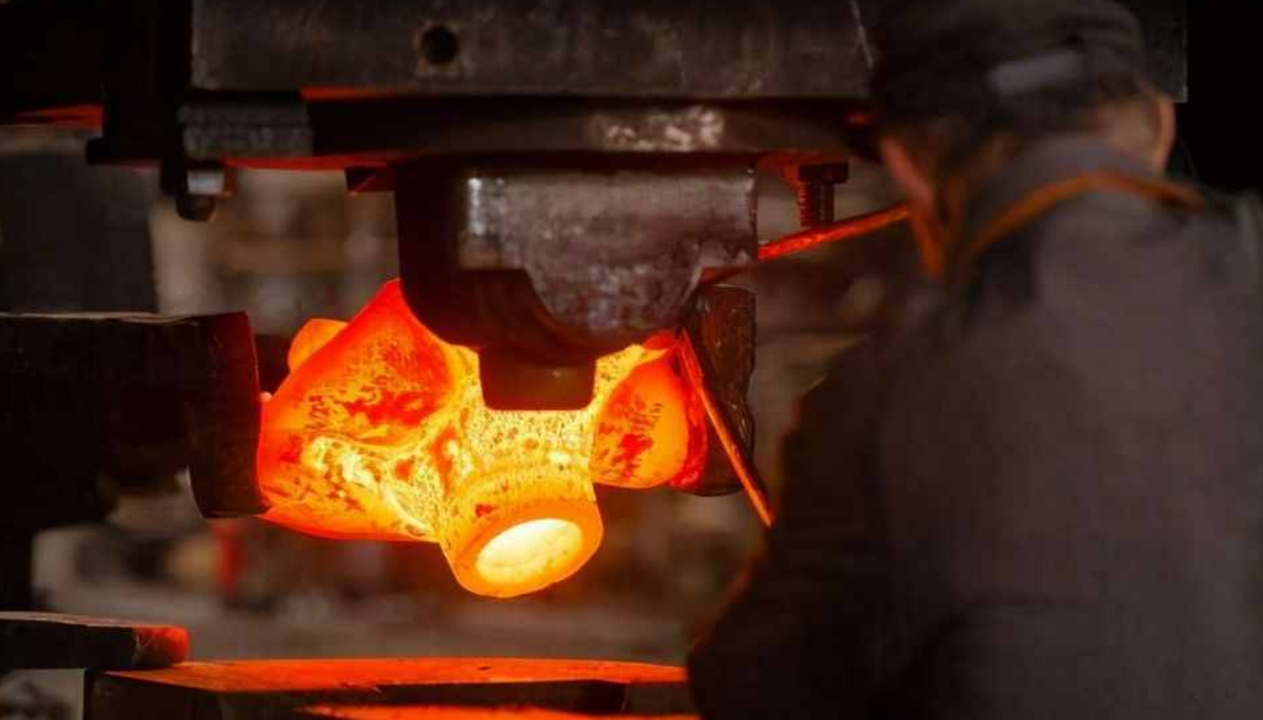
Forging is a processing method that uses forging machinery to exert pressure on metal blank to produce deformation so as to obtain forgings with certain mechanical properties, certain shapes and sizes. Forging (forging and stamping) is one of the two major components. Through forging, defects such as loose as cast can be eliminated in the process of metal smelting, and the micro structure can be optimized. At the same time, the mechanical properties of forgings are generally better than those of castings of the same materials because the complete metal streamline is preserved.

Deformation temperature
According to the deformation temperature, forging can be divided into hot forging (forging temperature is higher than the re-crystallization temperature of billet metal), warm forging (forging temperature is lower than the re-crystallization temperature of metal) and cold forging(room temperature). The re-crystallization temperature of steel is about 460℃, but 800℃ is generally used as the dividing line, higher than 800℃ is hot forging; Between 300 ℃ and 800℃ is called warm forging or semi-hot forging.
Closed die forging and closed heading
Because there is no flying edge in forging, the utilization rate of materials is high. It is possible to finish complex forgings with one or several processes. Since there is no flying edge, the forgings have less force area and less load required. However, it should be noted that the blank can not be completely restricted, so it is necessary to strictly control the volume of the blank, control the relative position of the forging die and measure the forging die, and try to reduce the wear of the forging die.
According to the way of the blank moving, forging can be divided into free forging, upsetting, extrusion, die forging, closed die forging, closed heading forging.
1. Free forging. Use the impact force or pressure to deform the metal between the upper and lower iron (anvil block) to obtain the required forgings, mainly manual forging and mechanical forging two kinds.
2. Die forging. Die forging is divided into open die forging and closed die forging. The metal blank is obtained by compression deformation in the forging die bore of a certain shape, which can be divided into cold heading, roll forging, radial forging and extrusion, etc.
-
PrevDevelopment trend of precision forging and forming process
-
NextNone